Significance
It is believed that a lack of experimental evidence (typical in the social sciences) slows but does not prevent the adoption of true theories. We evaluate this belief using a model of scientific research and promotion in which tenured scientists are slightly biased toward tenure candidates with similar beliefs. We find that when a science lacks evidence to discriminate between theories, or when tenure decisions do not rely on available evidence, true theories may not be adopted. The nonadoption of heliocentric theory in the 16th century, the persistence of bloodletting in the 19th century, the nonadoption of underconsumption theory in the early 20th century, and the persistence of radical mastectomy in the 20th century illustrate such risk.
Abstract
We develop a model describing how false paradigms may persist, hindering scientific progress. The model features two paradigms, one describing reality better than the other. Tenured scientists display homophily: they favor tenure candidates who adhere to their paradigm. As in statistics, power is the probability (absent any bias) of denying tenure to scientists adhering to the false paradigm. The model shows that because of homophily, when power is low, the false paradigm may prevail. Then only an increase in power can ignite convergence to the true paradigm. Historical case studies suggest that low power comes either from lack of empirical evidence, or from reluctance to base tenure decisions on available evidence.
Figure 1A: Dynamics of the share of Better scientists in the tenured population in a scientific field with high power
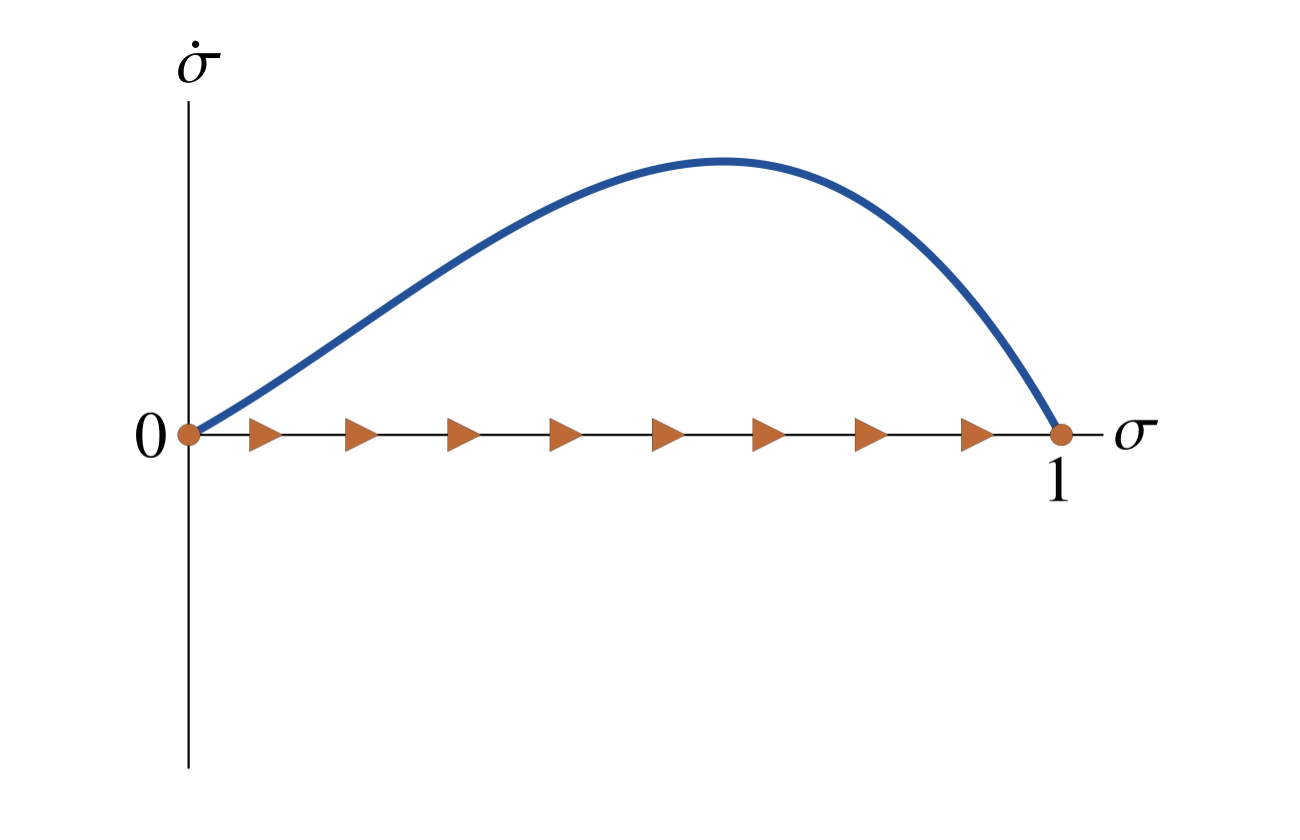
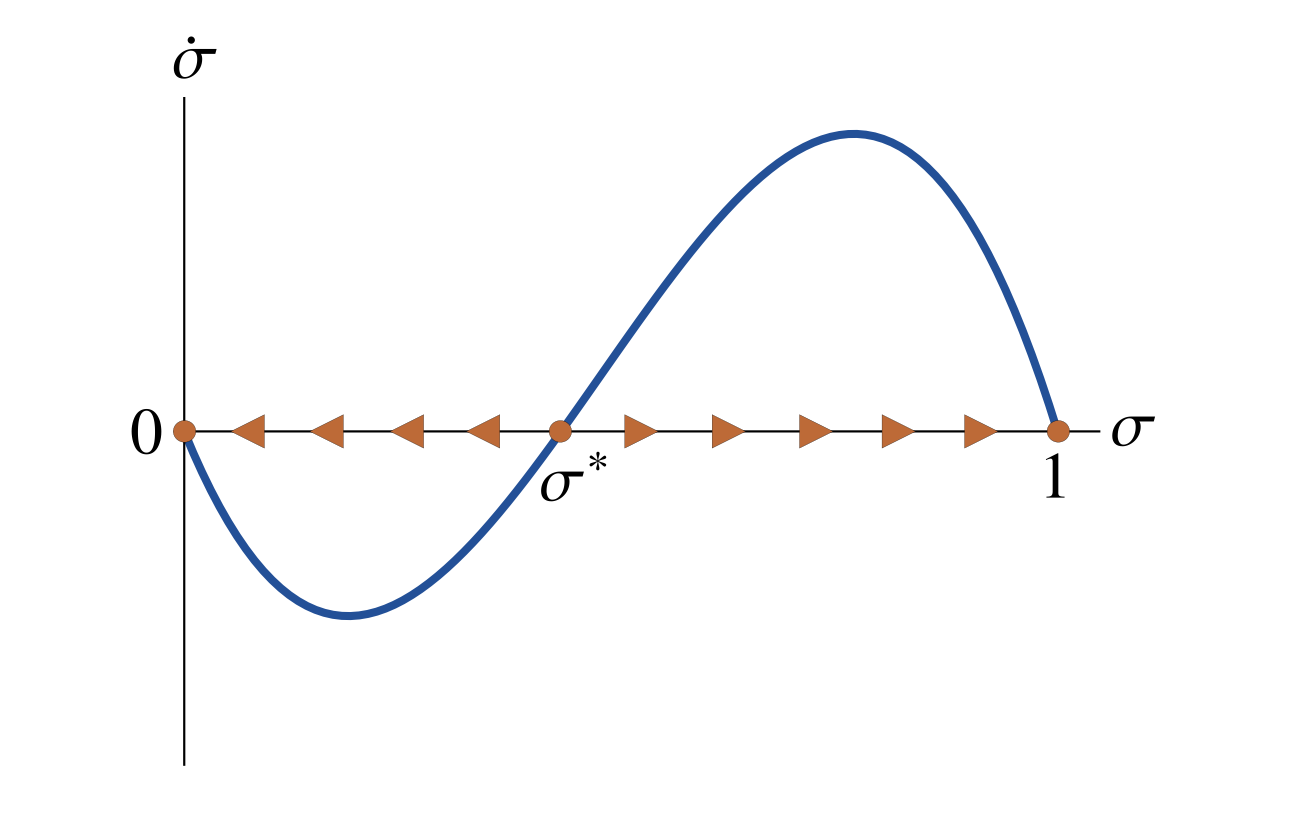
Figure 1B: Dynamics of the share of Better scientists in the tenured population in a scientific field with low power
Citation
Akerlof, George A., and Pascal Michaillat. 2018. “Persistence of False Paradigms in Low-Power Sciences.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115 (52): 13228–13233. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1816454115.
@article{AM18,
author = {George A. Akerlof and Pascal Michaillat},
year = {2018},
title = {Persistence of False Paradigms in Low-Power Sciences},
journal = {Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences},
volume = {115},
number = {52},
pages = {13228--13233},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1816454115}}
Related material
- Nontechnical summary for the Berkeley Initiative for Transparency in the Social Sciences
- Previous version of the paper (2017) – This version of the paper develops a heory of promotion based on evaluations by the already promoted. The already promoted show some favoritism toward candidates for promotion with similar beliefs, just as beetles are more prone to eat the eggs of other species. With such egg-eating bias, false beliefs may not be eliminated by the promotion system. An application is to the scientific process; another application is to hierarchical organizations. In organizations, egg-eating bias can result in the capture of the top of organizations by the wrong-minded.